Image
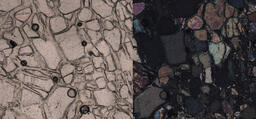
Key Characteristics: The mineral's lack of color, bird's eye extinction and high birefringence are all diagnostic 2V: 2Vx = 28 - 47° Relief: Moderate positive relief; Small change in relief upon stage rotation Cleavage: One perfect…
Image
Common Forms/Occurrences: Found in ultramafic igneous rocks and marbles formed from metamorphosed limestone Useful Identification Test: Gelatinizes in HCl Chemical formula: (Fe,Mg)2SiO4 Crystal System: Short crystals that may resemble sand grains…
Image
Common Forms/Occurrences: Present in most igneous and both regional and contact metamorphic rocks Useful Identification Test: Transparent to translucent Chemical formula: K(Mg,Fe)3(Al,Si3O10)(OH,F)2 Crystal System: Very short prisms that split…
Image
Common Forms/Occurrences: Common K-feldspar of pegmatites and hydrothermal veins; Prominent in granites Useful Identification Test: Demonstrates "tartan" twinning Chemical formula: KAlSi3O8 Crystal System: Translucent prisms with…
Image
Key Characteristics: Low relief, colorless nature, undulatory extinction and uniaxial character are diagnostic 2V: n/a Relief: Low positive relief Cleavage: None Colour and Plechroism: Colorless in thin section Optical Orientation: Undulatory…
Image
Key Characteristics: The high relief, lack of cleavage, crystal form and high birefringence are all diagnostic 2V: 2Vx = 46 - 98° Relief: High positive relief Cleavage: Cleavage not visible in thin section; Grains are commonly fractured and display…
Image
Common Forms/Occurrences: Common in dolomites and limestones Useful Identification Test: Soluble in H2SO4 with evolution of HF; slightly soluble in HCl Chemical formula: CaF2 Crystal System: Usually cubes Colour: Colourless, purple, blue, gray,…
Image
Mineralogical Composition: Intermediate; Quartz, Potassium Feldspar, Plagioclase Feldspar, Pyroxene, Amphibole, Biotite Texture (extrusive/intrusive): Extrusive; Aphantic: fine-grained Other distinctive properties: Dark gray to black; Found at…
Image
Mineralogical Composition: Visible crystals of two or more minerals in alternating light and dark foliated layers Texture (grain size, shape, sorting): Medium to coarse grained; Folitated Metamorphic grade: Intermediate Precursor rock: Mudstone,…
Image
Common Forms/Occurrences: Found as blocky crystals in basalts, gabbro, and andesites Useful Identification Test: Insoluble in HCl Chemical formula: calcium ferromagnesian silicate Crystal System: Short, 8-sided prisms Colour: Dark green to gray…
Image
Mineralogical Composition: Quartz sand grains fused together; grains will not rub off like sandstone, usually light colored Texture (grain size, shape, sorting): Fine to coarse grained; Nonfoliated Metamorphic grade: High Precursor rock: Sandstone…
Image
Texture (grain size, shape, sorting): Mostly sand (1/16 - 2mm grains). Composition (detrital, biochemical, chemical): Detrital sediment grains; derived from the mechanical and chemical weathering of continental rocks, which are comprised mostly of…
Image
Mineralogical Composition: Felsic, Intermediat, and Mafic; Muscovite, Quartz, Potassium Feldspar, Plagioclase Feldspar, Amphibole, Biotite; Olivine, Pyroxene Texture (extrusive/intrusive): Extrusive; Glassy Other distinctive properties: Dark green…
Image
Texture (grain size, shape, sorting): No visible grains; dark, very fine-grained rock, usually breaks with a conchoidal fracture Composition (detrital, biochemical, chemical): Biochemical sediment grains; shells and shell/coral fragments, and/or…
Image
Common Forms/Occurrences: Found in alabaster, satin spar, and selenite Useful Identification Test: Soft; Shows better cleavage than talc Chemical formula: CaSO4 ? 2H20 Crystal System: Tabular crystals, prisms, blades, or needles Colour: Colourless,…
Image
Key Characteristics: Relief which changes upon rotation of stage, extreme δ, rhombohedral cleavage and lamellar twinning are all diagnostic. Dolomite usually has higher refractive indices than calcite and may be colorless or iron stained where…
Image
Common Forms/Occurrences: Found near hot springs and volcanic regions Useful Identification Test: Identifiable odour when mixed with water (resembles rotton eggs) Chemical formula: S Crystal System: Transparent to translucent crystals or earthy…
Image
Common Forms/Occurrences: Found in granites and pegmatites Useful Identification Test: Can be split into thin flexible transparent sheets Chemical formula: KAl2(Al,Si3O10)(OH,F)2 Crystal System: Short opaque prisms Colour: Colourless, yellow, brown…
Image
Mineralogical Composition: Mostly visible crystals of amphibole Texture (grain size, shape, sorting): Medium to coarse grained; Folitated or Nonfoliated Metamorphic grade: High Precursor rock: Basalt, Gabbro, or Ultramafic igneous rocks Commercial…
Image
Mineralogical Composition: Black glossy rock that breaks along uneven or conchoidal fractures Texture (grain size, shape, sorting): Fine grained; Nonfoliated Metamorphic grade: High Precursor rock: Peat, Lignite, Bituminous coal Commercial…
Image
Common Forms/Occurrences: Secondary mineral formed by alteration of magnesium silicates (ie. Olivine and pyroxene) Useful Identification Test: Very soft to the touch, soapy feel Chemical formula: Mg3Si4O10(OH)2 Crystal System: Cryptocrystalline…
Image
Texture (grain size, shape, sorting): Rounded gravel, poorly sorted grains larger than 2mm Composition (detrital, biochemical, chemical): Detrital sediment grains; Rock fragments and/or quartz grains and/or feldspar grains and/or clay minerals Other…
Image
Texture (grain size, shape, sorting): Black, layered, brittle rock Composition (detrital, biochemical, chemical): Biochemical sediment grains; plant fragments and/or charcoal Other distinctive properties: May be sooty or bright Common depositional…
Image
Common Forms/Occurrences: In veins associated with other sulfide minerals Useful Identification Test: Decomposed by H2SO4 and by dilute HNO3 Chemical formula: PbS Crystal System: Forms cubes and octahedrons Colour: Silvery gray Streak: Gray to dark…