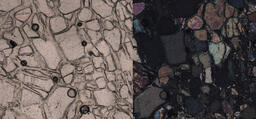
Image
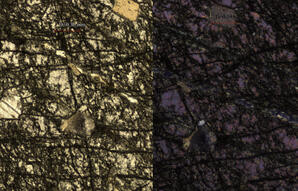
Key Characteristics: Two cleavages intersecting at 87 °, moderate birefringence and inclined extinction are key features 2V: 2Vz = 25 - 70° Relief: High positive relief Cleavage: Cleavages intersect at 87 ° Colour and Plechroism: Grains generally…
Image
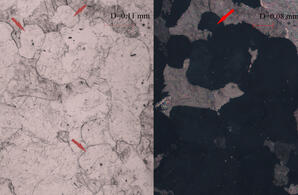
Key Characteristics: Moderate to high relief, lack of color, low birefringence and uniaxial character are key features 2V: n/a Relief: Moderate to high positive relief Cleavage: Not observed in thin section Colour and Plechroism: Most commonly…
Image
Common Forms/Occurrences: Mainly of sedimentary origin Useful Identification Test: May be attracted to a magnet after heating Chemical formula: Fe2O3 Crystal System: Thin tabular crystals or massive Colour: Silvery gray, black, or brick red Streak:…
Image
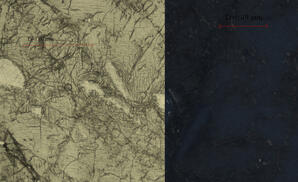
Key Characteristics: Two cleavages intersecting at 87 °, moderate birefringence and inclined extinction are key features 2V: 2Vz = 25 - 70° Relief: High positive relief Cleavage: Cleavages intersect at 87 ° Colour and Plechroism: Grains generally…
Image
Common Forms/Occurrences: Always of secondary origin resulting from the alteration of other ores or minerals containing iron Useful Identification Test: Hard or soft; Chemical formula: Fe2O3 ? nH2O Crystal System: Amorphous masses Colour: Yellow…
Image
Common Forms/Occurrences: Occurs in large masses in veins and pegmatites Useful Identification Test: Insoluble in acids except HF; soluble in molten Na2CO3 Chemical formula: SiO2 Crystal System: Hexagonal prism and pyramids Colour: Usually…
Image
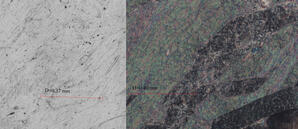
Key Characteristics: The mineral's lack of color, bird's eye extinction and high birefringence are all diagnostic; Talc is very similar to muscovite and is best distinguished by from muscovite by mineral association 2V: 2Vx = 0-30° Relief…
Image
Key Characteristics: Low negative relief, inclined extinction, low birefringence are key features 2V: 2Vz = 58° Relief: Low negative relief Cleavage: Two cleavages intersect at 42° and 138° Colour and Plechroism: Colorless in thin section Optical…
Image
Common Forms/Occurrences: Found in sedimentary strata; Formed secondarily from limestone Useful Identification Test: Will not effervesce in cold dilute acids; Powdered dolomite will however effervesce in warm acids Chemical formula: CaMg(CO3)2…
Image
Key Characteristics: The mineral's high relief, strong pleochroism, form and uniaxial character are diagnostic 2V: n/a Relief: Moderate to high positive relief Cleavage: Cleavage not visible in thin section; Grains are commonly fractured Colour…
Image
Common Forms/Occurrences: Principally occurs in metamorphic rocks ie. Crystalline limestones, schists, and gneisses or in hydrothermal veins Useful Identification Test: Opaque, relatively soft, non magnetic, and foliated Chemical formula: C Crystal…
Image
Common Forms/Occurrences: Widely distributed as accessory mineral (all classes of rocks) Useful Identification Test: Soluble in HNO3 or HCl Chemical formula: Ca5F(PO4)3 Crystal System: Hexagonal prisms Colour: Pale green or dark green, brown, blue,…
Image
Common Forms/Occurrences: Found in limestone, chalk, travertine, and onyx Useful Identification Test: Effervesces in dilute HCl Chemical formula: CaCO3 Crystal System: Prisms, rhombohedrons, or scalenohedrons that break into rhombohedrons Colour:…
Image
Common Forms/Occurrences: Occurs as extensive beds and irregular masses formed by evaporation of enclosed bodies of sea water Useful Identification Test: Salty taste; Chemical formula: NaCl Crystal System: Forms cubes and octahedrons Colour:…
Image
Common Forms/Occurrences: Widely distributed in mountian belts and deeply eroded shield areas of continental crust Useful Identification Test: Optically negative character and large optical axial angle and extinction angle Chemical formula: calcium…
Image
Key Characteristics: Low relief, colorless nature, polysynthetic twinning and oscillatory zoning are diagnostic of plagioclase 2V: 2Vx = 45 - 102° Relief: Low negative or positive relief Cleavage: Cleavages intersect at 93 °, usually not observed in…
Image
Key Characteristics: The mineral's lack of color, bird's eye extinction and high birefringence are all diagnostic 2V: 2Vx = 28 - 47° Relief: Moderate positive relief; Small change in relief upon stage rotation Cleavage: One perfect…
Image
Common Forms/Occurrences: Found in ultramafic igneous rocks and marbles formed from metamorphosed limestone Useful Identification Test: Gelatinizes in HCl Chemical formula: (Fe,Mg)2SiO4 Crystal System: Short crystals that may resemble sand grains…
Image
Common Forms/Occurrences: Present in most igneous and both regional and contact metamorphic rocks Useful Identification Test: Transparent to translucent Chemical formula: K(Mg,Fe)3(Al,Si3O10)(OH,F)2 Crystal System: Very short prisms that split…
Image
Common Forms/Occurrences: Common K-feldspar of pegmatites and hydrothermal veins; Prominent in granites Useful Identification Test: Demonstrates "tartan" twinning Chemical formula: KAlSi3O8 Crystal System: Translucent prisms with…
Image
Key Characteristics: Low relief, colorless nature, undulatory extinction and uniaxial character are diagnostic 2V: n/a Relief: Low positive relief Cleavage: None Colour and Plechroism: Colorless in thin section Optical Orientation: Undulatory…
Image
Key Characteristics: The high relief, lack of cleavage, crystal form and high birefringence are all diagnostic 2V: 2Vx = 46 - 98° Relief: High positive relief Cleavage: Cleavage not visible in thin section; Grains are commonly fractured and display…
Image
Common Forms/Occurrences: Common in dolomites and limestones Useful Identification Test: Soluble in H2SO4 with evolution of HF; slightly soluble in HCl Chemical formula: CaF2 Crystal System: Usually cubes Colour: Colourless, purple, blue, gray,…
Image
Common Forms/Occurrences: Found as blocky crystals in basalts, gabbro, and andesites Useful Identification Test: Insoluble in HCl Chemical formula: calcium ferromagnesian silicate Crystal System: Short, 8-sided prisms Colour: Dark green to gray…